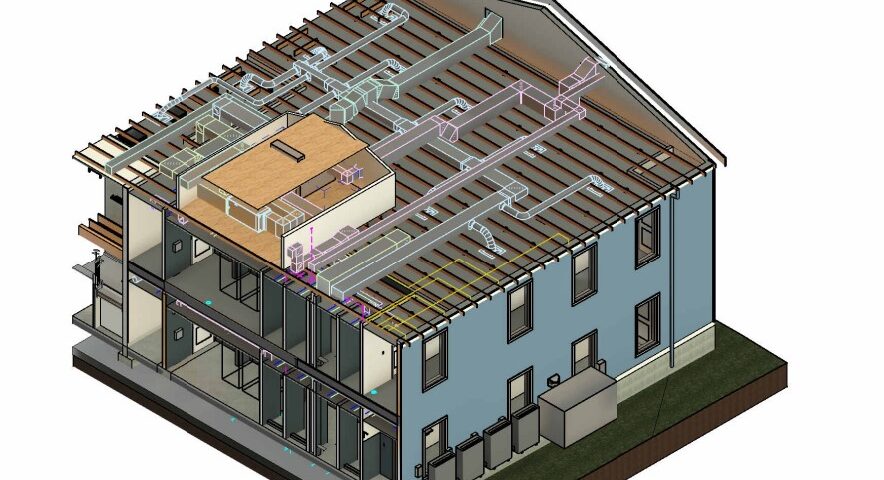
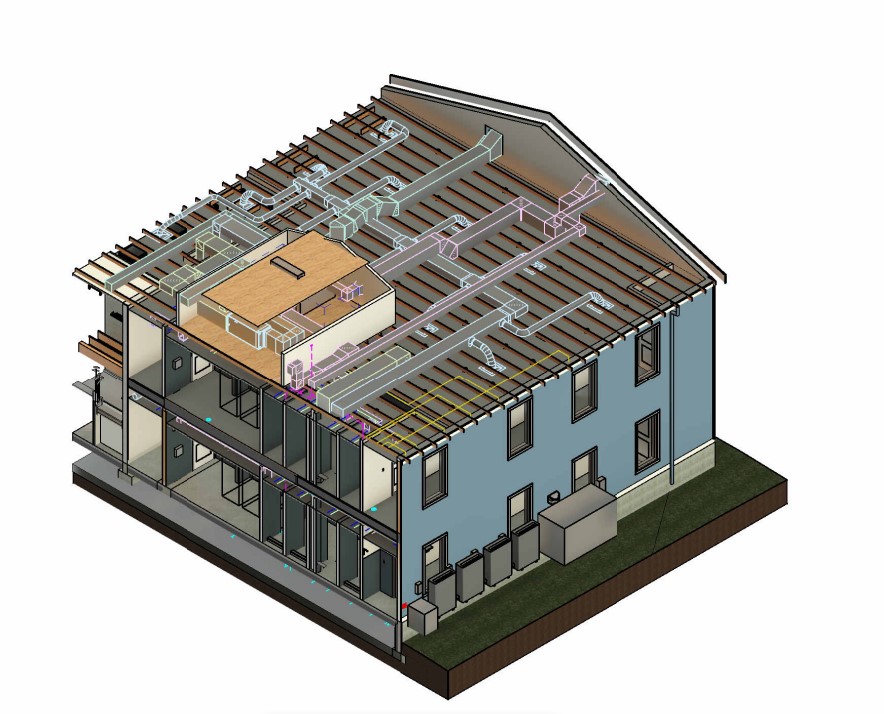
 Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a revolutionary tool in the realms of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), significantly influencing the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) domain. BIM’s influence is not just current but is evolving, with trends that are reshaping the industry today and predictions indicating a future rich with innovation.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a revolutionary tool in the realms of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), significantly influencing the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) domain. BIM’s influence is not just current but is evolving, with trends that are reshaping the industry today and predictions indicating a future rich with innovation.
- Cloud-Based BIM Collaboration: In MEP engineering, the use of cloud-based BIM collaboration tools enables seamless coordination among architects, engineers, and contractors. It helps to manage, share, and visualize data, reduce errors, and improve decision-making, thereby increasing overall project efficiency.
- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: Prefabrication and modular construction techniques, facilitated by BIM, allow MEP components to be designed and built off-site, then assembled or installed on-site. This process can reduce construction time, minimize waste, and increase quality and consistency.
- 3D Laser Scanning and Reality Capture: The MEP industry increasingly embraces 3D laser scanning and reality capture technologies for generating accurate as-built models of existing conditions, which is especially useful in renovation or retrofit projects. These models can be imported into BIM software to assist MEP engineers in integrating new systems with existing structures.
- BIM in Facility Management: BIM models help facility managers to efficiently maintain, repair, and operate the MEP systems in a building. These models provide a comprehensive view of the systems, making it easier to plan and manage maintenance activities and reduce downtime.
- BIM & the Internet of Things (IoT): When BIM is integrated with IoT, real-time data from connected devices in the MEP systems can be gathered and visualized. This allows facility managers to monitor system performance in real-time, foresee potential issues, and automate processes where possible. This integration ultimately enhances building efficiency and may even contribute to reducing energy consumption.
As BIM continues to evolve, here are some expected trends based on its current trajectory and emerging technologies:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Integration of AI and machine learning with BIM will become more prevalent. AI algorithms will analyze data from BIM models to optimize design, predict performance, and enhance decision-making. This will lead to more intelligent, efficient, and sustainable building designs. AI may also automate routine tasks, freeing up engineers and architects to focus on more complex issues.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The use of VR and AR in BIM will increase. Stakeholders will be able to immerse themselves in virtual models, enhancing understanding, and collaboration. This immersive experience will lead to better-informed decisions, reduced errors, and enhanced client engagement.
- Real-Time BIM: Real-time updating and accessibility of BIM models will become standard. As IoT becomes more integrated with BIM, real-time data from sensors will be incorporated into models. Enhanced monitoring and maintenance, real-time decision-making, and dynamic adaptability of building systems.
- Sustainability Integration: BIM will play a crucial role in sustainable design and construction practices, integrating tools and features that focus on energy efficiency, eco-friendly materials, and sustainable practices. More green buildings, reduced carbon footprint, and enhanced compliance with environmental regulations.
- Blockchain in BIM: Blockchain technology will be integrated with BIM to enhance security, traceability, and collaboration. Every change and transaction related to the BIM model can be securely recorded. Increased trust, reduced disputes, and enhanced data integrity.
- Customization and Personalization: Advanced BIM tools will allow more customization. End-users and clients will be involved in the design process, making real-time changes, and seeing immediate impacts. Enhanced client satisfaction, personalized designs, and increased demand for interactive BIM platforms.
- Regulatory Integration: BIM software will be equipped with features to automatically check designs against regulatory and compliance standards. Reduced legal issues, streamlined approval processes, and enhanced safety and compliance.
Bridging the Present and Future: BIM is already a cornerstone in enhancing collaboration, precision, and efficiency in the MEP and wider AEC sectors. The integration of emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and VR/AR with BIM is less about envisioning a distant future and more about preparing for imminent changes that will make project delivery more efficient, designs more sustainable, and buildings more adaptable.